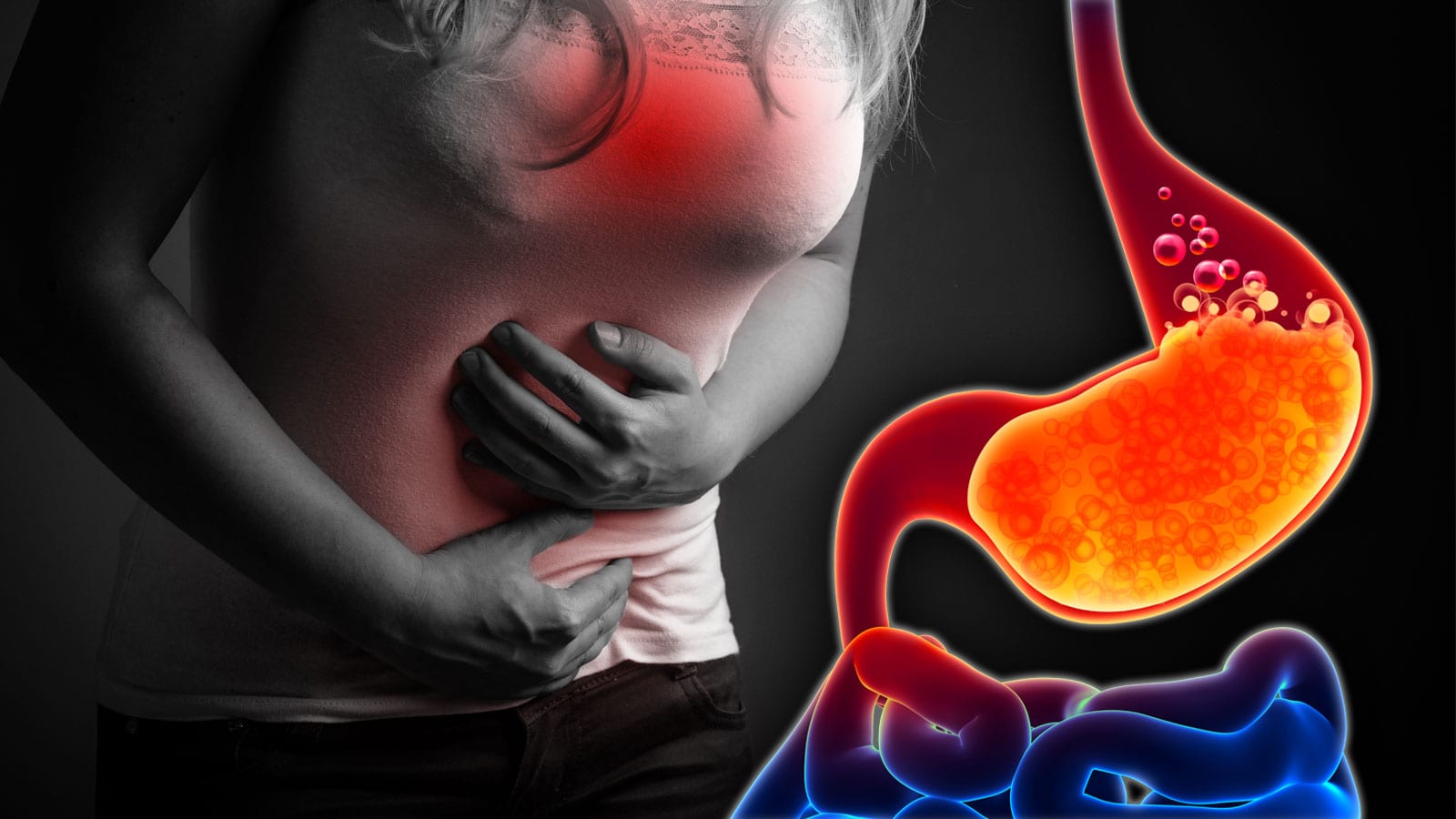
Acid reflux, also known as gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), is a chronic digestive condition where the liquid content of the stomach flows back into the esophagus. Here are some key points about acid reflux:
- Symptoms:
- Heartburn: The most common symptom, which feels like a burning chest pain starting behind the breastbone and moving upward to the neck and throat.
- Acidic or bitter taste: Some people experience this taste.
- Other symptoms include chest pain, difficulty swallowing, persistent dry cough, hoarseness, sore throat, regurgitation of food or sour liquid, and a sensation of a lump in the throat12.
- Causes:
- Frequent acid reflux occurs due to the backflow of stomach acid or bile into the esophagus.
- Risk factors include lower esophageal sphincter abnormalities, hiatal hernia, abnormal esophageal contractions, and slow stomach emptying1.
- Complications:
- Prevention and Lifestyle Changes:
- Eat smaller, more frequent meals.
- Lose weight if overweight.
- Find ways to relax.
- Avoid trigger foods (e.g., coffee, tomatoes, alcohol, chocolate, spicy foods).
- Do not lie down immediately after eating.
- Elevate your bed while sleeping.
- Quit smoking and limit alcohol intake1.
- Treatment Options:
- Over-the-counter medications (e.g., antacids, H-2 receptor blockers) to control stomach acid.
- Surgical options (e.g., Linx surgery, Nissen fundoplication) if symptoms persist1.

